Working Time
| Mon-Thu | 09:00 AM - 6:00 PM |
| Friday | 09:00 AM - 6:00 PM |
| Saturday | 09:00 AM - 2:00 PM |
| Sunday | Closed |
Request Form
Emergency Contact
Get Consultation
Acne Treatment
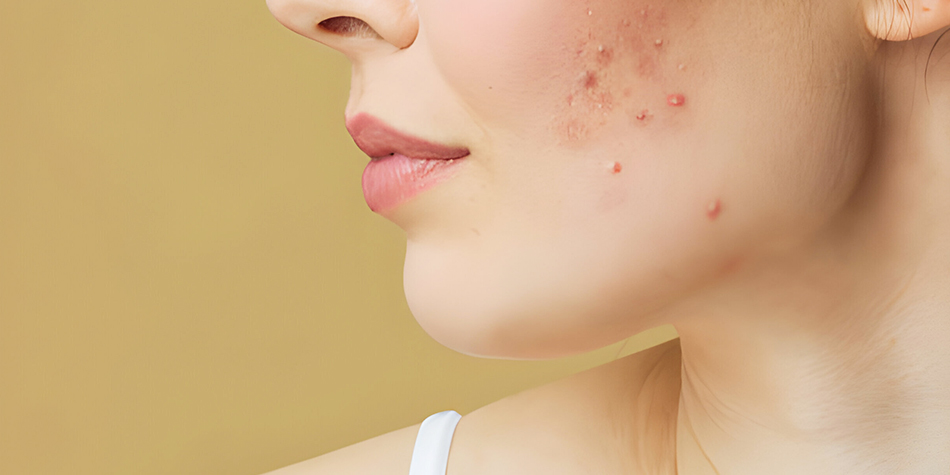
What is Acne?
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. It often results in the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts. Acne can affect people of all ages, but it is most common during adolescence due to hormonal changes.
Causes of Acne
Several factors can contribute to the development of acne, including:
- Excess Oil Production: Overproduction of oil (sebum) by the sebaceous glands can clog pores and lead to acne.
- Dead Skin Cells: Accumulation of dead skin cells can block hair follicles and contribute to the formation of acne.
- Bacteria: The presence of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria on the skin can exacerbate inflammation and acne.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger acne outbreaks.
- Genetics: Family history and genetics may play a role in predisposing individuals to acne.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as dairy products and high-glycemic-index foods, may exacerbate acne in some individuals.
Types of Acne
- Whiteheads: Closed plugged pores.
- Blackheads: Open plugged pores with a black appearance due to oxidation of melanin.
- Papules: Small, red, tender bumps.
- Pustules: Pimples containing pus at their tips.
- Nodules: Large, painful, solid lesions beneath the surface of the skin.
- Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring
Treatment Options
Treatment for acne depends on its severity and type. Common treatment options include.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription creams, gels, and lotions containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, retinoids, or antibiotics.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics, hormonal therapies (e.g., birth control pills), and isotretinoin (Accutane) may be prescribed for moderate to severe acne.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a skincare routine, maintaining good hygiene practices, and avoiding triggers such as harsh cosmetics and excessive sun exposure.
- Procedures: Dermatological procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, and extraction of comedones may be recommended for severe or persistent acne.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent acne entirely, you can minimize its occurrence by
- Washing your face regularly with a gentle cleanser.
- Avoiding excessive scrubbing or harsh skincare products.
- Keeping your hair clean and away from your face.
- Avoiding touching your face with dirty hands.
- Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated.
- Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques and regular exercise.
If you're struggling with acne, it's essential to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations and guidance tailored to your specific needs. With proper care and treatment, acne can be effectively managed, and clearer skin can be achieved.



